In what can be said as the biggest agricultural reform, the Union Govt. on June 5th passed an ordinance amending a 65 year-long act the Essential Commodities Act. The Govt. also paved the way for barrier-free trade between the states and also Contract Farming. We will give you our Vishleshan on these three decisions briefly in this article:
pic: swarajya
1. Amendment of Essential Commodities Act: According to this act, agricultural crops like pulses, cereals, onions, and other major crops fall under this act, which restricts the farmer to free trade of the crop and this orders him to sell his crop to a 'mandi' from where the majority portion is procured Food Corporation of India (FCI) and the rest by the dealers. This has become an absolute burden for the farmer as very often he is not able to get even the minimum support price(MSP). Now since the Govt. revoked pulses, cereals, and onion give farmers to sell his crop at any place he wishes to unlike before.
2. The Farmers Produce Trade and Commerce ordinance 2020: This gives the farmer an opportunity to sell his yield across the district and state borders without any trade barriers. It also opens doors for e-trading of the procure and all the seller need is a PAN card and any other Govt. authorized document. Although, it is noteworthy that this procedure comes under the State Govts authority and such a move will definitely have an impact on the states' income and their autonomy. But, the Centre believes that since it is for the progression of farmers, the state governments might accept this proposal. The States can question this move in the Judiciary.
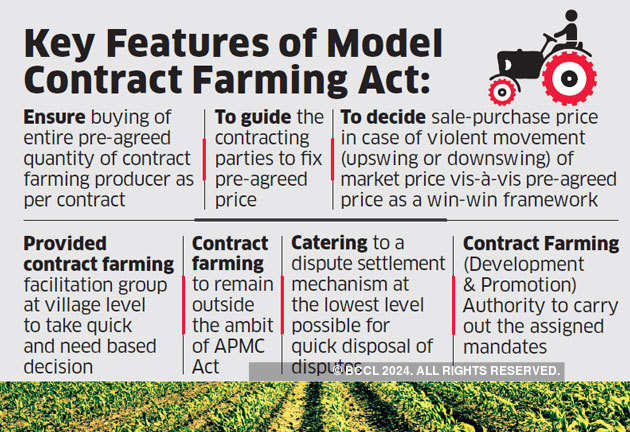
3. Contract Farming: This is a revolutionary decision taken by the Govt. It allows farmers to tie up with MNC's or any other third party organizations in the supply of the yield. Before the crop is sown the farmer and the Company can get into an agreement whereby, the company may allocate a certain sum to the farmer to organize his tools, fertilizers, seeds, etc. and can ask for a particular crop to be grown. The Company stipulates a certain rate to the yield beforehand and can also help the farmer in advanced farming techniques. To simplify this, Say you are a farmer with a 2-acre land and I own a Tomato Sauce company. I can get into an agreement with you that only I can purchase the yield from you for a certain amount. This agreement will be done even before the crop is sown. By this agreement, I can suggest the type of fertilizer, seeds to be used to the tomato crop. I can also give you a sum which would be helpful in raising the crop.
Though, there are few dangers associated with this method that the farmer could be cheated easily by the MNC in terms of the amount paid and say god forbid due to a calamity crop gets damaged and the MNC might trouble the farmer. But, the Govt. has said it is going to bring stipulated rules and regulations to address these possibilities.
Abhishek Reddy
Please subscribe to never miss an article from us.
Follow us on Instagram for the latest updates Samaj-Visahleshan

This could bring up some felicitous prosperity to our farmers.
ReplyDeleteNice vishleshan..
Keep it up..